MXT: A New Variant of Pyramid Vision Transformer for Multi-label Chest X-ray Image Classification
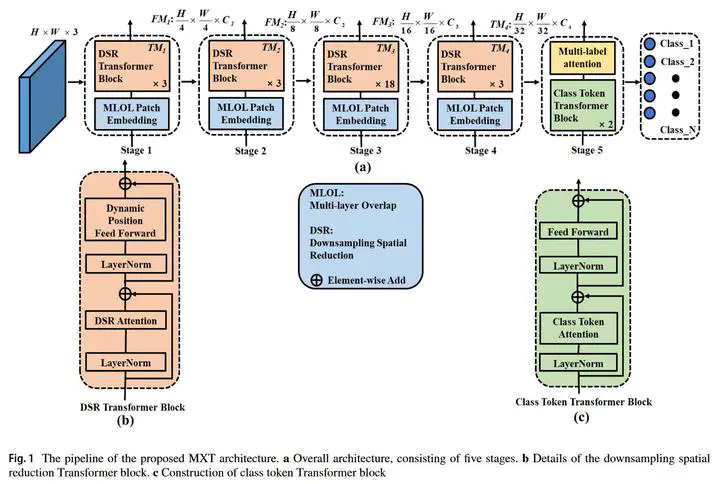 Image credit: Cognitive Computation
Image credit: Cognitive ComputationAbstract
Nowadays, the global COVID-19 situation is still serious, and the new mutant virus Delta has already spread all over the world. The chest X-ray is one of the most common radiological examinations for screening catheters and diagnosis of many lung diseases, which plays an important role in assisting clinical diagnosis during the outbreak. This study considers the problem of multi-label catheters and thorax disease classification on chest X-ray images based on computer vision. Therefore, we propose a new variant of pyramid vision Transformer for multi-label chest X-ray image classification, named MXT, which can capture both short and long-range visual information through self-attention. Especially, downsampling spatial reduction attention can reduce the resource consumption of using Transformer. Meanwhile, multi-layer overlap patch (MLOP) embedding is used to tokenize images and dynamic position feed forward with zero paddings can encode position instead of adding a positional mask. Furthermore, class token Transformer block and multi-label attention (MLA) are utilized to offer more effective processing of multi-label classification. We evaluate our MXT on Chest X-ray14 dataset which has 14 disease pathologies and Catheter dataset containing 11 types of catheter placement. Each image is labeled one or more categories. Compared with some state-of-the-art baselines, our MXT can yield the highest mean AUC score of 83.0% on the Chest X-ray14 dataset and 94.6% on the Catheter dataset. According to the ablation study, we can obtain the following results: (1) The proposed MLOP embedding has a better performance than overlap patch (OP) embedding layer and non-overlap patch (N-OP) embedding layer that the mean AUC score is improved 0.6% and 0.4%, respectively. (2) Our demonstrate dynamic position feed forward can replace the traditional position mask which can learn the position information, and the mean AUC increased by 0.6%. (3) The mean AUC score by the designed MLA is more 0.2% and 0.6% than using the class token and calculating the mean scores of all tokens. The comprehensive experiments on two datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method for multi-label chest X-ray image classification. Hence, our MXT can assist radiologists in diagnoses of lung diseases and check the placement of catheters, which can reduce the work pressure of medical staff.