Contrastive learning with token projection for Omicron pneumonia identification from few-shot chest CT images
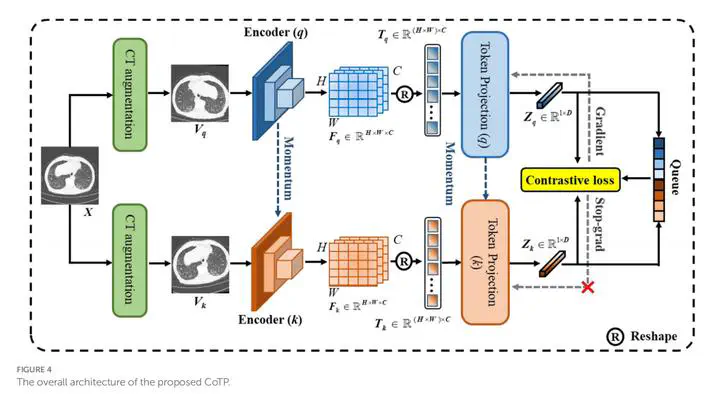 Image credit: Frontiers
Image credit: FrontiersAbstract
Deep learning-based methods can promote and save critical time for the diagnosis of pneumonia from computed tomography (CT) images of the chest, where the methods usually rely on large amounts of labeled data to learn good visual representations. However, medical images are difficult to obtain and need to be labeled by professional radiologists.To address this issue, a novel contrastive learning model with token projection, namely CoTP, is proposed for improving the diagnostic quality of few-shot chest CT images. Specifically, (1) we utilize solely unlabeled data for fitting CoTP, along with a small number of labeled samples for fine-tuning, (2) we present a new Omicron dataset and modify the data augmentation strategy, i.e., random Poisson noise perturbation for the CT interpretation task, and (3) token projection is utilized to further improve the quality of the global visual representations. The ResNet50 pre-trained by CoTP attained accuracy (ACC) of 92.35%, sensitivity (SEN) of 92.96%, precision (PRE) of 91.54%, and the area under the receiver-operating characteristics curve (AUC) of 98.90% on the presented Omicron dataset. On the contrary, the ResNet50 without pre-training achieved ACC, SEN, PRE, and AUC of 77.61, 77.90, 76.69, and 85.66%, respectively. Extensive experiments reveal that a model pre-trained by CoTP greatly outperforms that without pre-training. The CoTP can improve the efficacy of diagnosis and reduce the heavy workload of radiologists for screening of Omicron pneumonia.