 Image credit: Elsevier
Image credit: ElsevierAbstract
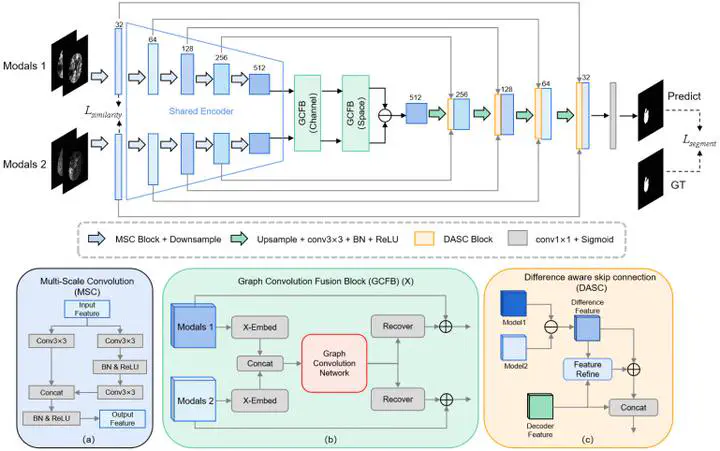
Stroke segmentation has great significance for clinical diagnosis and timely treatment. Medical images of strokes often come in the form of multiple modalities. But most existing methods simply stack these modalities as input, disregarding the connections and other clinical prior knowledge associated with each modality. In this paper, we present MDANet, a multimodal difference aware network for stroke segmentation based on multimodal input. The proposed network mainly consists of a difference aware module and a graph convolution fusion block. In the difference aware module, a parameter-shared encoder is adopted to extract features from different modality groups and generate difference feature maps by subtracting one group from another to enhance the perception of potential lesion areas. We further design a similarity loss to improve this ability. The graph convolution fusion block is developed to aggregate features from different modalities with a channel embedding strategy to model the features globally and a space embedding strategy for local modeling. The MDANet is trained and evaluated on the Ischemic Stroke Lesion Segmentation (ISLES) 2018 and 2022 datasets. Our approach achieves a dice score of 58.34 and 70.44, surpassing the performance of other advanced existing methods.